At the Snapdragon Tech Summit 2022, Qualcomm presented its fastest mobile processor to date, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2. Compared to its predecessor, the new system-on-chip (SoC) primarily offers significantly higher AI performance, from which a wide variety of functions benefit. Game developers, on the other hand, can use hardware-accelerated real-time ray tracing and add more realistic graphics to their titles. It should be possible to check how convincing this effect really is in the end and how much performance it requires this year: Qualcomm expects the first smartphones with the new processor to be available by the end of 2022.
For the first time with INT4
The numerous changes compared to the predecessor Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 show that artificial intelligence was a focus in the development of the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2. Qualcomm has revised the hexagon processor primarily responsible for this area at several points. The tensor unit is now twice as large and for the first time a Snapdragon chip supports INT4 calculations in addition to INT8, INT16 and FP16.
Also new is Micro Tile Inferencing. This allows data to be broken down into smaller parts and distributed to the tensor, vector, and scalar units at the same time. According to Qualcomm, this increases the accuracy of the predictions, among other things.
All in all, the AI performance should be more than four times as high – Qualcomm specifically speaks of a factor of 4.35 – as before. On the other hand, there is also an increase in efficiency. Performance per watt improved by 60 percent on certain calculations.

AI is one of the most important aspects of the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2. Last but not least, the significantly larger tensor unit and the Micro Tile Inferencing available for the first time increase the performance of the artificial intelligence.
(Image: Qualcomm)
In addition to the hexagon processor, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 also has other AI processors. For the first time, Qualcomm is using two such helpers in the so-called Sensing Hub – previously there was only one. The Sensing Hub is responsible for controlling numerous sensors and various background activities. For example, smartphones with the new Snapdragon chip should be able to recognize QR codes with the camera even when the display is switched off. If, on the other hand, the front camera detects that someone else is looking at the display next to you, the system can prevent push notifications if you wish – this provides a little more privacy. But there is also talk of improvements with regard to language assistants. In the future, the system will recognize activation words such as “Hey, Google” more precisely.
Apps that translate in real time can take advantage of the advanced AI capabilities. Among other things, the SoC should make it possible to output spoken language in real time in several other languages.
More AI for more beautiful photos
But one of the most important uses for many smartphone users should also benefit from the AI innovations: taking photos. In this context, Qualcomm speaks of the Snapdragon Sight platform, which includes the Spectra ISP image processor and the Hexagon processor, among other things. This enables image optimization in real time – with simultaneous subdivision of the recording into different areas (multiple semantic segmentation). Among other things, the artificial intelligence recognizes individual parts of a face or separates the different objects from one another in landscape photos. This allows objects to be tweaked separately, rather than just making adjustments to the entire image. Other side effects of the higher AI performance are improvements in low-light shots and in the creation of artificial blur (bokeh).
In addition, Qualcomm has optimized the Spectra ISP for new image sensors. Specifically, the company is calling the Samsung Isocell HP3 with 200 megapixels, which was presented in June 2022, which, among other things, can focus faster and enables multi-level merging of pixels (pixel binning). The sensor combines four pixels into one for 50-megapixel photos, and 16 pixels for 12.5-megapixel photos instead. Pixel binning is primarily intended to ensure a higher recording quality in poor lighting conditions.
Another innovation: for the first time, a Snapdragon chip supports the AV1 codec for playing 8K videos at 60 frames per second. Recordings, on the other hand, are possible in 8K at 30 frames per second. If you reduce the resolution to 4K, the maximum frame rate increases to 120. In slow motion mode, the chip records up to 960 frames per second – but then only with 1280 × 720 pixels. In addition, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 offers the technical requirements to record HDR videos. With HLG, HDR10, HDR10+ and Dolby Vision, it supports all the important variants. If you wish, you can save the recordings as 10-bit HEVC video, images in 10-bit HEIC format.
Faster speed for 5G and WiFi
If you not only want to process data locally on the smartphone, but also share it with others, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 achieves higher speeds than its predecessors, according to Qualcomm, with the Snapdragon Connect platform announced at IFA 2022. The components of the platform are the 5G modem Snapdragon X70 and the communication unit FastConnect 7800.
In appropriately developed networks, the 5G modem supports transmission rates of up to 10 Gbit/s in the downlink and 3.5 Gbit/s in the uplink and, thanks to the integrated AI processor, should enable lower latencies and more stable connections. In addition, the Snapdragon X70 makes it possible for the first time to actively operate two 5G connections in parallel in dual SIM operation.
FastConnect 7800, on the other hand, primarily accelerates data exchange in the WLAN. It supports Wi-Fi 7 and is said to transmit up to 5.8 Gbit/s at its peak. Dual Bluetooth is also available. Ideally, Qualcomm wants to double the Bluetooth range and accelerate the connection between the smartphone and Bluetooth accessories. Supported audio codecs for Bluetooth connections include aptX Lossless, aptX Adaptive and Bluetooth LE Audio.
Vulkan 1.3 and hardware raytracing for the graphics unit
But Qualcomm has also revised the more classic processor components. The Adreno graphics unit now achieves up to 25 percent higher performance, and when using the Vulkan interface, the increase should be up to 30 percent. For the first time, Qualcomm supports Vulkan 1.3 – as well as the interfaces OpenGL ES 3.2 and OpenCL 2.0 FP. But work was also done on efficiency. Ideally, the graphics unit needs 45 percent less energy.
For gamers, on the other hand, the hardware-accelerated real-time ray tracing should be, with which developers can install more realistic reflections and lighting effects, among other things. However, the graphics unit only supports ray tracing in conjunction with Vulkan 1.3. However, Qualcomm did not initially reveal any technical details about the ray tracing hardware – these should follow in the course of the Snapdragon Tech Summit 2022. But not only Qualcomm enables ray tracing on smartphones. The MediaTek Dimensity 9200 presented at the beginning of November also supports this thanks to the integrated graphics unit Immortalis G715 from ARM.
With real-time ray tracing, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 should enable more realistic graphics in games. The first developers have already announced support.
(Image: Qualcomm)
A more realistic representation should also enable the support of the Metahumans framework of the Unreal Engine 5. Qualcomm did not announce which developers will use the framework. This is different with ray tracing: According to the information, Tencent and NetEase Games, among others, want to make use of it. The graphics unit also offers other innovations. The Adreno GPU now also supports Adaptive HDR and, thanks to OLED Aging Compensation, should prevent burn-in effects on OLED displays. This is an algorithm that ensures that the individual pixels are used more evenly.
The Adreno controls the displays built into the smartphone in a maximum of 4K resolution with 60 frames per second, alternatively in QHD+ with 144 frames per second. Hardware decoders are available for videos in H.265 and VP9 formats. With HLG, HDR10, HDR10+ and Dolby Vision, the graphics unit supports the playback of all relevant HDR variants.
Faster CPU cores
But there is also something new in the CPU part of the smartphone chip. Qualcomm took over the general structure with three performance levels and a total of eight cores from the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1, but partially changed the number of cores per level.
It remains with a prime core, which is based on the ARM Cortex-X3 instead of the Cortex-X2 as before. The maximum clock rate increases from almost 3 to 3.19 GHz. In addition, there are now four instead of three performance cores as in the predecessor. Two are Cortex-A710, the other two are Cortex-A715. The reason for this mix: The Cortex-A715 cores do not offer native 32-bit support, but Qualcomm does not want to do without it in the performance level. The clock limit increases from 2.5 to 2.8 GHz.
Less demanding computing tasks are now handled by three instead of four efficiency cores, which are Cortex-A510 refreshes. This achieves 2 instead of 1.8 GHz.
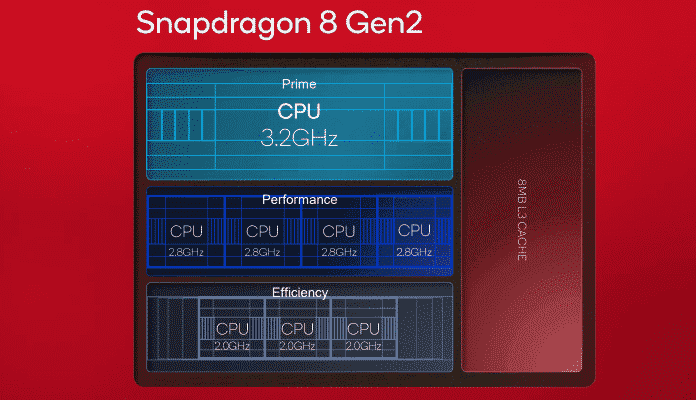
With the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2, Qualcomm sticks to eight cryo cores in the CPU design, but uses new models and enables higher clock rates.
(Image: Qualcomm)
In total, the CPU performance should be up to 35 percent higher than with the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1. Qualcomm claims to have improved the efficiency by up to 40 percent.
If you use your smartphone with headphones to play music or videos, Dynamic Spatial Audio can be an interesting innovation. This is surround sound, but it takes into account the movement of the head or the headphones. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 takes over the corresponding calculations based on the movement data transmitted by the headphones.
Manufacturing in 4 nm at TSMC
Qualcomm has the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 manufactured by TSMC using 4-nanometer technology. Samsung was still able to get the order for the first generation of the Snapdragon 8, but TSMC was already responsible for its optimized version Snapdragon 8+ Gen 1. Asus, Honor, Sony and Xiaomi are among the first manufacturers to launch smartphones with the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2.
updates
11/16/2022
02:20
watch
We added details on Micro Tile Inferencing.
(pbe)

