Sunrises and sunsets can be very different. Sometimes the clouds glow in intense red and yellow tones. What conditions must be met for the sky to turn red?
The color of the sky is essentially determined by the scattering of sunlight. Scattering is the effect that the sun’s rays are deflected from their original direction of incidence. When this occurs on air molecules that are small compared to the wavelength of sunlight, it is called “Rayleigh scattering”. Their special feature is that different wavelengths are scattered to different degrees. Of the visible colors, blue light is scattered the most. It therefore reaches the observer from all possible directions and the sky appears blue. The lower the sun is, the longer the path of its rays through the atmosphere and the less blue there is in direct sunlight. That’s why the lower it is, the redder the sunlight is.
Due to this effect, the sun often rises and sets as a bright red ball when the sky is clear. But even more impressive are the sunrises and sunsets, when existing clouds turn red. This happens when the sun’s light illuminates a layer of clouds like a screen. The clouds have to be in the right place for this to happen. The most favorable situation is when the horizon in the direction of the sun is clear of clouds, but at the same time there are clouds near the observer. Then the red light reaches the bottom of the cloud. A red dawn with colorful clouds occurs when a low foothills approaches from the west and the eastern horizon is still cloud-free. Such a dawn is a harbinger of bad weather. In the evening, however, a cloud-free western horizon and red-lit clouds above the observer usually mean an improvement in the weather. Since the cloud cover conditions can be predicted, it is also possible for photographers with sufficient experience to visit photogenic vantage points in good time before the sky turns red and to set the alarm clock in case of dawn. However, the distance from the observer that the sky must be clear of clouds for the red sunlight to find its way to the observer depends on the height of the clouds.
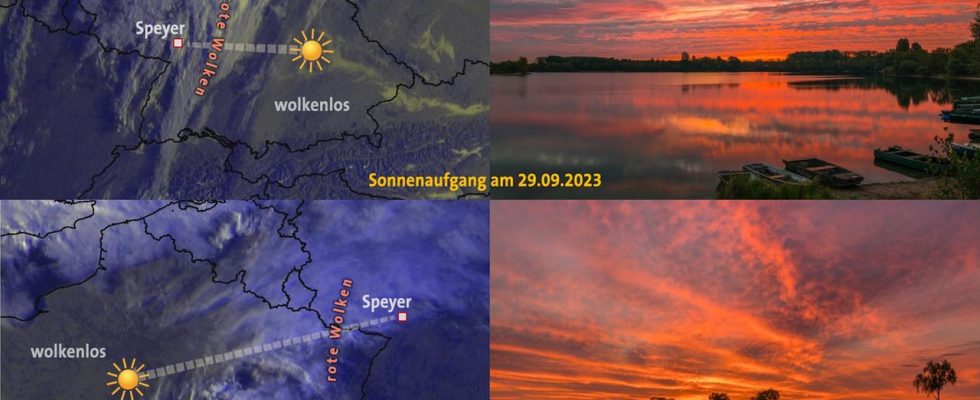
If there are deep clouds above you, the sunlight cannot reach 50 kilometers. This means that there is no red color even if the sky is clear of clouds only 50 kilometers away from the sun. With medium-high clouds, sunlight can travel much further distances below a cloud layer. An example of this is shown in the top two images in our figure. At sunrise on September 29, 2023, there was altocumulus clouds about 4 kilometers high over Speyer. At the same time, the sky over Bavaria was cloudless. The clouds glowed an intense red, as the photo shows. Experience has shown that such medium-level clouds still turn red even when the edge of the cloud is around 200 kilometers away from the observer.
When clouds are high, there are sometimes surprisingly large distances to the cloud-free area, where the clouds still turn red. An example of this is shown in the two images below in our illustration. On October 16th there was a 7 kilometer high cirrostratus over the Palatinate. The sky was only clear of clouds in the middle of France in the Paris area and south of there. In this situation, the distance to the edge of the cloud was around 450 kilometers as the crow flies. Nevertheless, an intense afterglow could be observed. If you had less experience, you wouldn’t necessarily have guessed from looking at a satellite image that there would be enough sunset in this situation.
To estimate whether there will be red clouds, several things are important. The photographer must have experience with how far away the cloud-free area can be. But he also has to know the direction in which he has to look on a satellite image or on the maps of weather models to forecast clouds. In winter the sun in Germany rises southeast of the observer, and in summer it rises in the northeast. The direction of sunset varies between southwest and northwest throughout the year. It is often not easy to estimate how high the cloud layer actually is. There are often several layers of clouds on top of each other, which makes things complicated. An experienced meteorologist is still significantly better at predicting red clouds than apps that are now available for this purpose.