Space travel
NASA probe is the first spacecraft to touch the sun
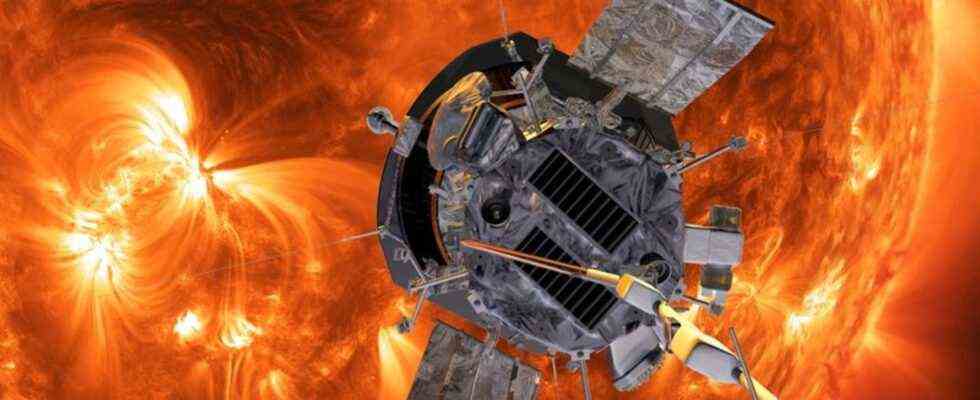
The computer graphic shows the “Parker Solar Probe” probe of the US space agency Nasa on its way to the sun. Photo: – / AP / dpa
© dpa-infocom GmbH
With a probe called “Parker Solar Probe”, NASA wants to find out more about our solar system. The missile is about the size of a small car and can withstand extreme heat and radiation.
The NASA “Parker Solar Probe” probe flew through the outer atmosphere of the sun and, according to the US space agency, was the first spacecraft to touch this star.
Nasa announced that the probe had examined particles and magnetic fields in the so-called solar corona. The first flight through the solar corona took only a few hours, and further flights are planned.
NASA manager Thomas Zurbuchen spoke of a “monumental moment” and a “remarkable achievement”. “This milestone will not only give us deeper insights into how the sun is formed and how it affects the solar system, but everything we learn about our own star will also teach us more about stars in the rest of the universe.”
Carbon armor twelve centimeters thick
The “Parker Solar Probe” launched in August 2018 came closer to the sun just a few months later than any other spaceship before. At that time, the probe had moved closer than 42.7 million kilometers to the sun, breaking the record set up in April 1976 by the German-American “Helios 2” probe. Since then, the “Parker Solar Probe” has come closer to the sun and now circles around it in large elliptical orbits.
Protected by an almost twelve centimeter thick carbon armor, the approximately 7,000 kilogram probe, the size of a small car, is said to have to withstand more heat and radiation than any previous missile. The NASA researchers hope that the mission, which is scheduled to run until 2025, will provide information about why the corona is many times hotter than the surface of the sun and thus also about how stars work. The data could also make future weather forecasts more accurate.