The DART probe is expected to impact Dimorphos on Tuesday night.
© NASA/Johns Hopkins APL
That DART spacecraft crashed shortly after on Tuesday 2 a.m – if everything goes right. At 6 kilometers per second (22,000 km/h) it will Asteroid moon Dimorphos ram. The aim of the DART mission is to orbit to change the celestial body. In the future, asteroids that are on a collision course with Earth could be deflected in this way.
“It is one historical mission“, says Nancy Chabot, Head of DART Coordination, at a press event. DART stands for “Double Asteroid Redirection Test”.
The binary asteroid is dimorphoswho the asteroid Didymos orbited like a moon at a distance of one kilometer. The two are approaching Earth at maximum 7.1 million kilometers.
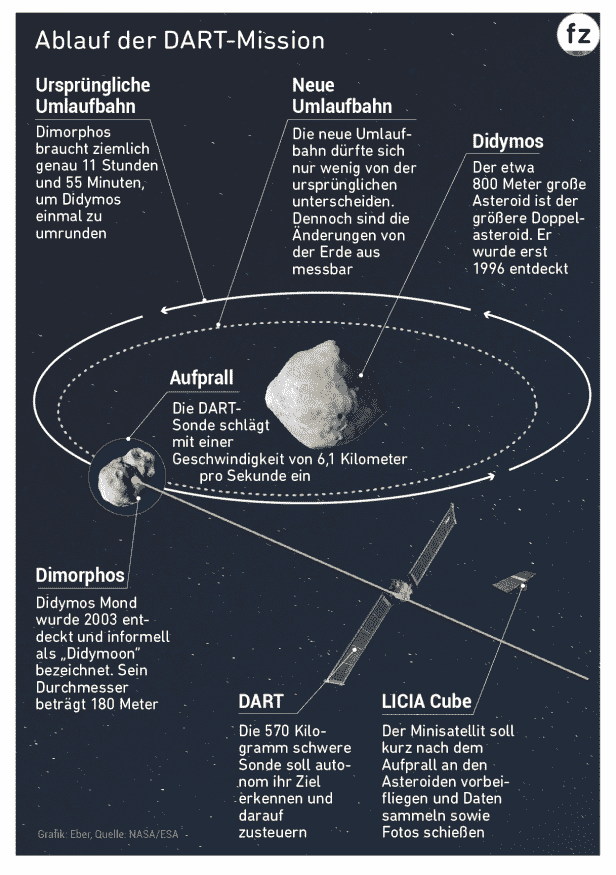
The course of the DART mission.
© ESA/futurezone
“There was never any danger that they could collide with the ground,” Chabot points out. However, the double asteroid offers the possibility of ramming the smaller celestial body and measuring its deflection.
Minimal distraction expected
“The impact deflects Dimorphos only slightly,” explains NASA scientists Tom Statler. Nevertheless, it is hoped that the new orbit can be calculated from Earth. This is done by measuring time. It takes Dimorphos pretty much exactly to orbit its neighbor 11 hours and 55 minutes. If the orbit narrows after the impact, as planned, the time will be shorter.
“You can feel like a wristwatch imagine it running too fast or too slow,” says Statler: “You may not notice it at first, but after a few weeks you realize that it’s going wrong.” So it will also take researchers on Earth some time to understand to determine how much the asteroid was deflected. Already few percentage points would already be a success.
Autopilot controls DART probe
However, it is immediately clear whether Dimorphos was hit. “The DART probe sends one image per second to Earth,” says Ian Carnelli by the European Space Agency ESA, which is also involved in the mission. “In the last few seconds before impact should tennis ball-sized objects be visible on the surface of Dimorphos – and then hopefully nothing more.”
The probe is not steered from the ground, but by an autopilot. So shall DART Dimorphos recognize independently and head towards it. “There’s a small chance that we’ll miss the asteroid, but it’s really not that big,” says Statler.

The DART probe (in gold) on Earth, being loaded into the SpaceX shipping container
© NASA/JPL-Caltech
Satellite is to deliver the first images
The small satellite collects more data on the impact LICIACube, which was replaced by the actual DART probe almost 2 weeks ago. He will 3 minutes after impact fly past Dimorphos. “It’s going to be a very quick flyby,” says Simone Pirrotta by the Italian space agency ASI.
Nevertheless, one hopes to gain insights from it. So should the one thrown up by the impact cloud of dust more about the composition of the asteroid betrayed. Pictures from the back are also important 3D model to create the object.
Hera mission starts in 2024
On November 24, 2021, DART embarked on their kamikaze mission. In a few years that will come European space probe “Hera” comes into play: it should be in the December 2026 reach the binary asteroid and accompany it for several months. One miniprobe should even land on Dimorphos. “Images can be deceiving,” says Carnelli, who directs the mission. “The mission will allow us to measure the mass and composition of Dimorphos and better determine what it takes to deflect an asteroid.”
Protection from near-earth objects
That one day it will be necessary to remove an asteroid from his collision course nobody at NASA and ESA hopes to distract with the earth. “Objects with a diameter of 150 meters or more can locally severe devastation cause and also have global implications,” says Statler.
“We estimate that we only know about 40 percent of near-Earth objects of this size.” concrete data whether it will be possible to protect oneself from potentially dangerous asteroids in the future.
binary asteroids
15 percent of the asteroids travel in pairs. They are held together by their gravity, much like the earth and moon.
Hera mission
ESA’s Hera spacecraft is scheduled to leave Earth in 2024 and reach the asteroids in 2026. Their investigation focuses primarily on the resulting crater.
62 megatons
Dynamite is the equivalent of the explosive force of an asteroid about 100 meters in diameter impacting the earth’s surface. That is roughly equivalent to the strength of 4,600 Hiroshima atomic bombs.

