Wikimedia commons
The Hyalomma marginatum tick is present in the south of France, around the Mediterranean.
HEALTH – If you don’t like little creatures, the tick Hyalomma marginatum should give you a cold sweat. Especially since it is a… “giant” tick. Present on the French Mediterranean rim for around ten years – and for decades in Corsica – this mite does not transmit Lyme disease, but Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever.
As the summer season approaches, and the risks of being bitten increase, we take stock of this disease, which, for the moment, has not affected humans in France.
An 8mm tick
This virus is transmitted by a “giant tick”. Measuring around 8mm, it is up to twice the size of a standard tick, depending on UFC-Que Choisir. Already established in warm regions of Asia, Africa, the Middle East and the Balkans, it is now present in the departments of Pyrénées-Orientales, Aude, Hérault, Gard, Ardèche, Drôme, Bouches-du-Rhône, Var, Alpes-Maritimes and the two departments of Corsica.
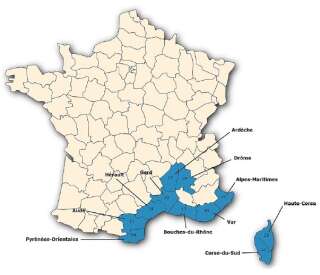
Public health France
The presence map of the Hyalomma marginatum tick in mainland France.
According to Santé Publique France (SPF), which published an alert last May, it was in October 2023 that Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever was detected for the first time in France, on cattle, in the Pyrénées-Orientales and in Corsica. “ Even though bites by this tick are rare, they can occur and cause infection in humans.noted public health agencywho adds that around ten infections have been detected in Spain in humans since 2016.
What is Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever?
This infection is caused by a virus, which can cause several symptoms: fever, but also chills and digestive problems. In rare cases, the virus causes hemorrhagic illness with uncontrolled bleeding, which can lead to death. It is most often transmitted by a tick bite. Hyalomma marginatum. It is also possible to contract it through contact with the blood of an infected animal or person, which remains very rare.
To find out if you are contaminated after an injection, Santé Publique France advises you to pay attention, in the following fourteen days, if you suddenly feel a fever, headache or pain in your muscles and joints. If this is the case, consult a doctor. “In the 30 days following the bite, other symptoms may appear, linked to
other tick-borne diseases »adds the agency.
How to avoid infection?
The best way to avoid catching the virus is obviously not to be bitten by a tick. And to avoid bites, there are preventive measures. You should first know that the risks of being bitten are exacerbated during spring and summer, in dry areas of scrubland and scrub, pastures, hiking trails, fields, crops, orchards or even vineyards.
If you have the idea of walking in these places, SPF recommends wearing light-colored clothing (to better see the tick), covering the limbs, and wearing closed shoes. It is also advisable to regularly inspect your body and that of your children. “As skin repellents have limited effectiveness, their use should not replace the preventive measures cited above”specifies the agency.
Finally, SPF recommends having a tick remover or fine tweezers to remove the little creature yourself quickly during a bite. And if you do not have these tools, it is advisable to remove it with your fingers – protecting them with a tissue –, taking it as close as possible to the skin, then disinfect. SPF also advises taking a photo of the mite to show it to the doctor.
Also see on HuffPost :

