counselor
From A to C: These are the differences between the USB cable types
With the many USB cable types, consumers quickly lose track
© Roman Mykhalchuk / Getty Images
Few things are more annoying than not having the right cable to hand in the heat of the moment. The guide explains what types of USB cables there are and how they differ.
How nice it would be if every electrical device used the same plug. In fact, the European Union is working to enforce the USB-C connector as a uniform charging standard by the end of 2024. The rule will apply to mobile phones, tablets, digital cameras, headphones, headsets, portable consoles, portable speakers, e-readers, keyboards, mice, earphones and portable navigation devices and laptops.
This makes sense in any case, as the law avoids electronic waste and the consumer avoids unnecessary costs for cables and/or chargers. Until then, we still have to deal with different types of USB cables. The most common in 2023 are:
- USB A
- USB B 2.0
- USB B 3.0
- USB mini
- USB Micro 2.0
- USB Micro 3.0
- USB-C
Important: There are, of course, various subtypes of each presented as USB Mini A. But they are extremely rare.
USB cable types: These are the differences The different USB types at a glance. © Tymofii Malynovskyi / Getty Images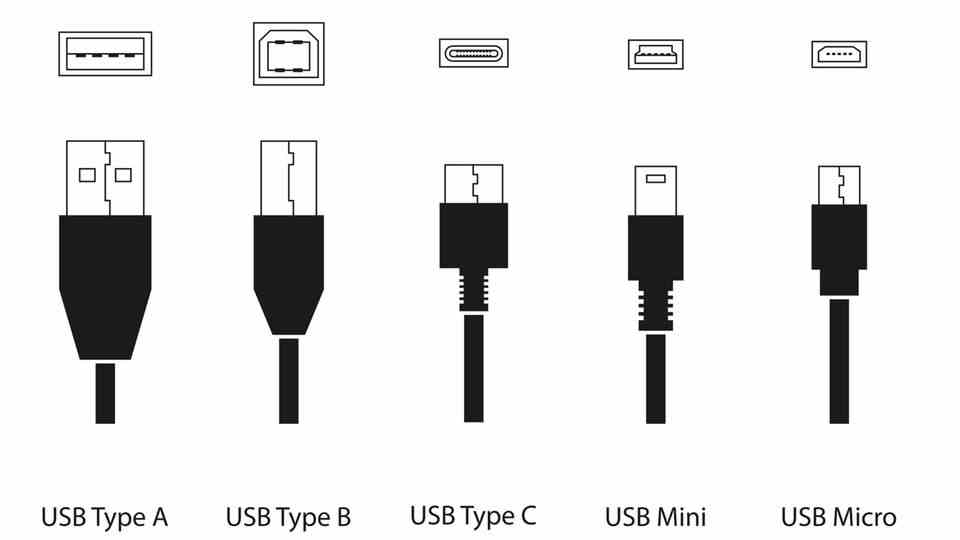
The cable types differ in their appearance and were originally designed for different purposes. Probably the most well-known USB type is USB A. It’s the chunky, square USB connector that’s still commonly found on laptops and computers.
The USB B type is now used less frequently. It is mostly found on monitors that have a USB hub. The monitor connects to the computer and forwards the data from the USB hub.
Important Here’s the distinction between USB 2-B and 3-B because the fit is different. Very old external hard drives or printers still work USB 2 B.
USB mini is a smaller version of USB Type-B. It was developed for smaller products such as cameras or game console controllers, because a normal USB port on these devices would be too bulky and large. USB Mini-B only supports the USB 2.0 protocol and is therefore obsolete.
An even smaller form of USB connection is USB micro. Compared to Mini-USB, Micro-B also supports USB 3.0 protocol. USB-Micro-B can mainly be found on older Android smartphones, e-book readers or cameras.
Although Micro-USB supports the USB 3.0 protocol, it looks different: That USB micro 3.0 cable is a bit bulkier than its 2.0 counterpart.
USB-C is the latest USB type that combines the strengths of its predecessor generations. The connector is oval and flat, making it suitable for laptops, computers, tablets and smaller devices such as smartphones and cameras. In addition, USB-C supports every USB protocol and newer Thunderbolt sockets are also wrapped in the guise of the USB-C connection.
USB cable types are not the same as USB protocols
A common misconception about USB connections is that USB-C is generally faster than USB-A or B. It is true that USB-C is the newest type of USB. What is wrong is that the latest USB type always works with the latest USB protocol. Because only the USB protocol decides how quickly, for example, computers and external SSDs exchange data.
A USB-A socket, for example, can work with the USB 3.2 protocol and a USB-C socket only has USB 3.1. The protocols are all compatible, but can slow each other down: a USB-A stick with USB protocol 2.0 also transfers data to a USB-A 3.0 socket – but much more slowly than a USB 3.0 stick would do. The table reveals how much slower.
protocol | transfer rate |
USB2.0 | 480Mbps |
USB 3.1 (or also 3.0) | 5 Gbps |
USB 3.1 x2 (3.1 Gen 2): | Dual Lane, 2 x 5Gbps |
USB 3.2 (Gen 1) | 10 Gbps |
USB 3.2 x2 (Gen2): | Dual Lane 2x 10 Gbit/s |
usb 4 | 40 Gbps |
USB connections are not only suitable for exchanging data. The interface also charges mobile end devices or forwards image signals from the laptop to the monitor. Unfortunately, not every socket can do everything, which is why manufacturers sometimes label the inputs. A double “S” on the socket indicates that it can supply power to an end device.
“DP”, on the other hand, stands for Display Port and means that image signals can be forwarded. Unfortunately, manufacturers are free to label their USB ports, and very few do. For example, if you are looking for a USB-C monitor that both charges the laptop and forwards image signals via its USB-C socket, you have to take a close look before you buy.
Tip: Magnetic USB-C charging cable
If you are only looking for a charging cable for your smartphone, this is the one for you magnetic USB-C cable at. Danger: Such a cable does not transfer data! It consists of a magnetic head, which is plugged into the USB-C socket of the device to be charged, and the cable, which finds its place in the charger. The advantage of this is that the cable and smartphone come loose if you trip over them, for example. Apple users are familiar with the magnetic charging connection from the MagSafe connector on their MacBooks.
Sources:European Parliament, heise.de, usb.org
You might also be interested in:
This article contains so-called affiliate links. Further information are available here.